Diabetes Management: A Guide to Living Well
Diabetes Management
Demystifying Diabetes: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
Living with diabetes can feel overwhelming at first. But with the right knowledge, tools, and support system, you can not only manage it effectively but also thrive.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the information you need to understand the different types of diabetes, explore their causes and risk factors, and navigate crucial aspects of management.
We’ll delve into healthy eating strategies, unlock the power of exercise, and discuss the importance of regular blood sugar monitoring.
Finally, we’ll address the emotional aspects of living with diabetes and offer valuable tips for building a strong support system to empower your journey.
Unveiling the Different Forms of Diabetes:
There are three main types of diabetes, each with its unique characteristics:
-
Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune condition disrupts the pancreas’ ability to produce insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing beta cells, leaving individuals with type 1 dependent on lifelong insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: The most prevalent form, affecting over 90% of diabetes cases, type 2 diabetes arises when either the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or the cells become resistant to its effects. The initial stages may be manageable through diet and exercise modifications, but some individuals may require oral medications or injectable insulin for optimal control.
-
Gestational Diabetes: This temporary form of diabetes develops during pregnancy in some women. The hormonal fluctuations of pregnancy can impair insulin sensitivity, leading to high blood sugar levels. Gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth, but it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Delving Deeper: Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetes:
Understanding the reasons behind different types of diabetes empowers you to make informed choices and possibly prevent its onset. Let’s explore the causes and risk factors in detail:
-
Type 1 Diabetes: While the exact cause of type 1 remains elusive, a combination of genetics and environmental factors is believed to play a role. Family history and certain genes can predispose individuals to type 1 diabetes. Additionally, environmental triggers like viral infections or exposure to certain chemicals in early life might be involved.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: Here, the risk factors are more clearly defined and offer opportunities for prevention or delay:
- Family History: Having a parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes significantly increases your risk.
- Weight: Carrying excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, puts a strain on insulin’s effectiveness. Losing weight, even a modest amount, can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle is a major contributor to insulin resistance. Regular physical activity helps your body use insulin more effectively.
- Diet: A diet rich in processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance. Opting for whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients and promotes healthy blood sugar levels.
- Race or Ethnicity: Certain ethnicities, including African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, Native Americans, and Asian Americans, have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, but it can develop at any stage of life.
- Gestational Diabetes: If you’ve had gestational diabetes, you’re more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS are at an increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes due to hormonal imbalances.
Living with Clarity: Symptoms and Management Strategies:
Early diagnosis and effective management are crucial to prevent complications associated with diabetes. Let’s explore the symptoms and dive into key management strategies:
Common Symptoms:
- Frequent Urination: The body attempts to eliminate excess sugar from the bloodstream through increased urination.
- Excessive Thirst: The body tries to compensate for the lost fluids through frequent urination, leading to increased thirst.
- Increased Hunger: Even after eating, high blood sugar levels can send hunger signals due to the body’s inability to utilize glucose effectively for energy.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: When the body cannot properly utilize glucose for energy, it may begin to break down muscle and fat tissues, leading to unintended weight loss.
- Fatigue: Chronic high blood sugar levels can deplete energy levels, causing fatigue and tiredness.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to blurred vision.
- Slow-healing Wounds: High blood sugar can impair circulation and the immune system’s ability to fight infection, leading to delayed wound healing.
- Frequent Infections: High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system’s ability to fight off bacteria and fungi, increasing the risk of infections.
Management Strategies:
-
Dietary Triumphs: A well-balanced diet is the cornerstone of diabetes management. Here are some key principles:
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. These foods provide essential nutrients, fiber, and sustained energy without spiking blood sugar levels.
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods are often loaded with refined carbohydrates, unhealthy fats, and added sugars, all of which can negatively impact blood sugar control.
- Embrace Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid consuming excessive calories that can contribute to weight gain and worsen insulin resistance.
- Read Food Labels: Become familiar with food labels to understand carbohydrate content, sugar content, and fiber content. This empowers you to make informed choices that align with your diabetes management goals.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that considers your preferences, lifestyle, and blood sugar control needs.
-
The Power of Movement: Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for diabetes management:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise helps your body utilize insulin more effectively, leading to better blood sugar control.
- Weight Management: Physical activity burns calories and aids in weight management, which is crucial for type 2 diabetes management.
- Overall Health: Exercise strengthens your heart, improves circulation, and boosts overall well-being.
- Aim for Moderate-Intensity Activity: Strive for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Brisk walking, swimming, cycling, and dancing are all excellent options.
- Find Activities You Enjoy: Choose activities you find enjoyable to make exercise a sustainable part of your routine.
- Start Gradually: If you’re new to exercise, begin slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity over time.
-
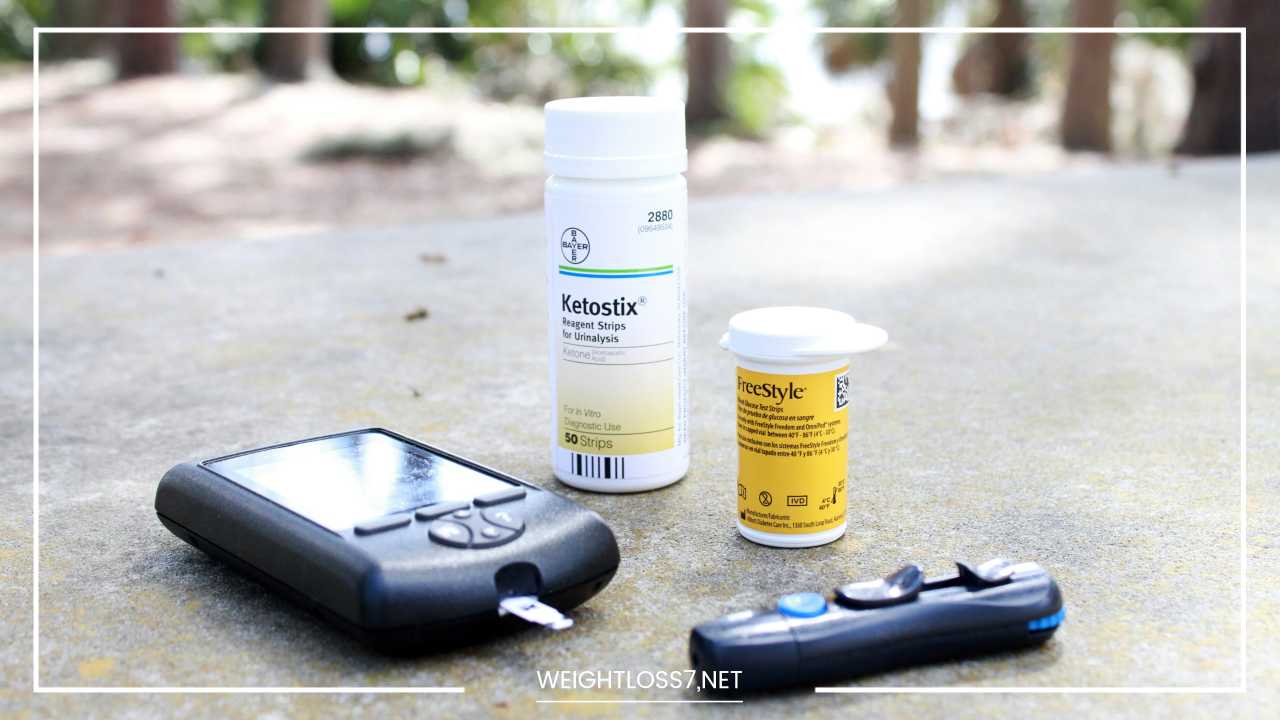
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Your Trusted Guide: Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels provides valuable insights into how your body reacts to food, exercise, and medications. This empowers you to make informed decisions and adjust your management strategies as needed:
- Frequency of Monitoring: Talk to your doctor about how often you should check your blood sugar levels based on the type and severity of your diabetes.
- Target Ranges: Your doctor will establish target blood sugar ranges for you. Monitoring helps you stay within these ranges to minimize complications.
- Different Monitoring Tools: Various blood sugar monitoring tools are available, such as finger pricking meters and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs). Discuss with your doctor which option is best for you.
-
Medication Adherence: Your Partner in Control: If your doctor prescribes medications for your diabetes, it’s crucial to take them exactly as directed. These medications can help manage your blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
- Different Medication Types: Medications for diabetes can include oral medications like metformin and injectable insulin.
- Understanding Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects of your medications and talk to your doctor if you experience any concerns.
- Maintaining a Routine: Develop a routine for taking your medications to ensure you don’t miss any doses.
Beyond Blood Sugar: Addressing the Emotional Impact of Diabetes
Living with a chronic condition like diabetes can take an emotional toll. Here are some tips for managing the emotional aspects:
- Acknowledge Your Emotions: Don’t bottle up your feelings. Allow yourself to feel frustration, anger, or sadness. Talking to a therapist or counselor can be immensely helpful.
- Connect with Others: Join a diabetes support group or connect with others who understand the challenges you face. Sharing experiences and finding encouragement can be a great source of strength.
- Celebrate Your Victories: Focus on the positive steps you’re taking towards managing your diabetes. Celebrate even small victories, like sticking to your exercise routine or achieving a good blood sugar reading.
- Practice Self-Care: Make time for activities you enjoy, whether it’s reading, spending time in nature, or listening to music. Prioritizing self-care helps you manage stress and maintain emotional well-being.
Building Your Support System: A Circle of Strength
A strong support system is vital for navigating the journey with diabetes. Here’s how to build it:
- Family and Friends: Open up to your loved ones about your diagnosis and enlist their support. Educate them about diabetes so they can understand your needs and offer encouragement.
- Healthcare Team: Your doctor, registered dietitian, diabetes educator, and other healthcare professionals form a crucial part of your support system. They provide guidance, answer your questions, and work collaboratively with you to develop a personalized management plan.
- Diabetes Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand your challenges can be incredibly beneficial. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences, learn from each other, and find encouragement. Online and in-person support groups are available, allowing you to choose the option that best suits your needs.
- Online Communities: Online communities dedicated to diabetes can be a valuable source of information, support, and inspiration. Join credible online forums and social media groups to connect with others, learn new tips, and stay updated on the latest advancements in diabetes management.
Living a Fulfilling Life with Diabetes:
Diabetes doesn’t have to define your life. With knowledge, effective management strategies, and a strong support system, you can achieve optimal health, prevent complications, and live a full and vibrant life.
Remember, you’re not alone on this journey. Embrace the power of self-care, celebrate your victories, and focus on living a healthy and fulfilling life.
Exploring Potential Complications and Long-Term Management Strategies
While diabetes management focuses on maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, it’s crucial to understand potential complications and long-term strategies to minimize their risk.
Potential Complications of Diabetes:
Chronically high blood sugar levels can damage various organs and systems in the body if left unmanaged. Here’s a look at some potential complications:
- Heart Disease and Stroke: Diabetes significantly increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the formation of plaque, leading to narrowed arteries and potential blockages.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): High blood sugar can damage nerves throughout the body, causing pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness. This can affect your feet, hands, and other areas.
- Foot Problems: Nerve damage and poor circulation in the feet can increase the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and even amputation. Proper foot care is essential for people with diabetes.
- Kidney Disease: Diabetes can damage the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease and potentially kidney failure.
- Eye Problems: High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of blindness in adults.
- Skin and Mouth Problems: People with diabetes are more prone to skin infections and slow-healing wounds. Additionally, they may experience dry mouth and increased risk of gum disease.
Long-Term Management Strategies for Optimal Health:
By adopting a proactive approach and implementing long-term management strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve your overall well-being:
- Regular Checkups and Screenings: Schedule regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your blood sugar levels, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other health markers. Additionally, undergo recommended screenings for diabetic retinopathy, kidney disease, and foot problems.
- Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle remains paramount. Prioritize a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep. These habits contribute significantly to diabetes management and overall health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen blood sugar control. Practice stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to manage stress effectively.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking significantly increases the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to improve your health.
- Staying Informed: Keep yourself updated on the latest advancements in diabetes research and treatment options. Talk to your doctor about new technologies like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and potential future developments in diabetes management.
Remember: Early detection, effective management, and a commitment to healthy living are the cornerstones of preventing complications and thriving with diabetes.
Living a Balanced Life with Diabetes
Diabetes management isn’t just about restrictions and limitations. It’s about empowering yourself to make informed choices and embrace a healthy lifestyle that allows you to live a fulfilling life. Here are some tips for achieving a healthy balance:
- Focus on Progress, Not Perfection: Aim for progress, not perfection. There will be setbacks along the way, but don’t let them discourage you. Celebrate your successes, learn from challenges, and keep moving forward.
- Make Healthy Choices Fun: Find ways to make healthy choices enjoyable. Explore new recipes, discover activities you enjoy, and involve loved ones in your healthy lifestyle journey.
- Don’t Isolate Yourself: Diabetes doesn’t have to isolate you. Stay connected with loved ones, participate in activities you enjoy, and don’t be afraid to seek support.
- Embrace Life’s Celebrations: Don’t deprive yourself of occasional treats and celebrations. Learn to make healthy substitutions and enjoy special occasions without compromising your overall management plan.
By following these tips and incorporating the valuable information provided throughout this blog post, you can take control of your diabetes, live a healthy and fulfilling life, and achieve your full potential.

















