Medical Imaging Tests 101: Everything You Need to Know

Medical Imaging Tests
Seeing Beneath the Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Imaging Medical Tests
Our bodies are intricate machines, a symphony of interconnected systems that, when functioning properly, keep us healthy and vibrant.
But sometimes, a discordant note disrupts the harmony. Aches, pains, and unusual symptoms can be the first signs of trouble brewing beneath the surface.
This is where medical imaging steps in, acting as a powerful tool for doctors to peer inside and diagnose the root cause of the issue.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of medical imaging. We’ll explore the various types of imaging tests available, how they work, their specific uses, and what you can expect during the procedures.
By understanding these incredible technologies, you’ll feel more empowered and informed when discussing imaging with your doctor.
The Power of Seeing Inside: Why Imaging Tests Matter
Medical imaging has revolutionized modern medicine. Before these technologies, diagnosing internal issues relied heavily on physical examinations and potentially invasive procedures.
Imaging tests offer a safe, non-invasive way to visualize internal organs, bones, tissues, and even blood flow. This newfound ability to see inside translates into several crucial benefits for patients:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Imaging tests can pinpoint fractures, tumors, bleeding, blockages, and other abnormalities with remarkable precision. This accurate diagnosis allows doctors to identify the exact cause of your symptoms and recommend the most appropriate treatment course.
- Treatment Planning: Detailed visuals from imaging studies play a vital role in treatment planning. For instance, an MRI scan of the brain helps surgeons map the location of a tumor before surgery, leading to more precise and successful procedures.
- Monitoring Treatment: Imaging tests can be used to track the effectiveness of treatment. For example, a CT scan taken after chemotherapy can show if a tumor has shrunk, indicating the treatment’s success.
- Early Detection: Certain imaging tests, like mammograms and colonoscopies, are used for screening purposes. Early detection of diseases like cancer allows for prompt intervention, significantly improving treatment outcomes and patient survival rates.
Beyond the X-Ray: A Spectrum of Imaging Technologies
The world of medical imaging isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Doctors have a diverse arsenal of imaging tools at their disposal, each with its unique strengths and applications. Here’s a closer look at some of the most commonly used imaging tests:
-
X-Ray (Radiography): The veteran of the group, X-rays are the simplest and most widely used imaging test. They utilize invisible electromagnetic waves to capture images of dense tissues like bones and some organs. X-rays are quick, painless, and effective for diagnosing fractures, pneumonia, and joint problems.
-
Ultrasound: This technology uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of soft tissues like muscles, organs, and blood vessels. Ultrasound is painless, doesn’t involve radiation, and is particularly useful for examining pregnancies, internal bleeding, and gallstones. It can also be used to guide procedures like needle biopsies.
-
Computed Tomography (CT Scan): A CT scan takes X-ray imaging to the next level. It captures multiple X-ray images from different angles and then uses sophisticated computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional views of your body. CT scans are highly effective for diagnosing internal injuries, tumors, and blood vessel abnormalities. However, they involve a small amount of radiation exposure.
-
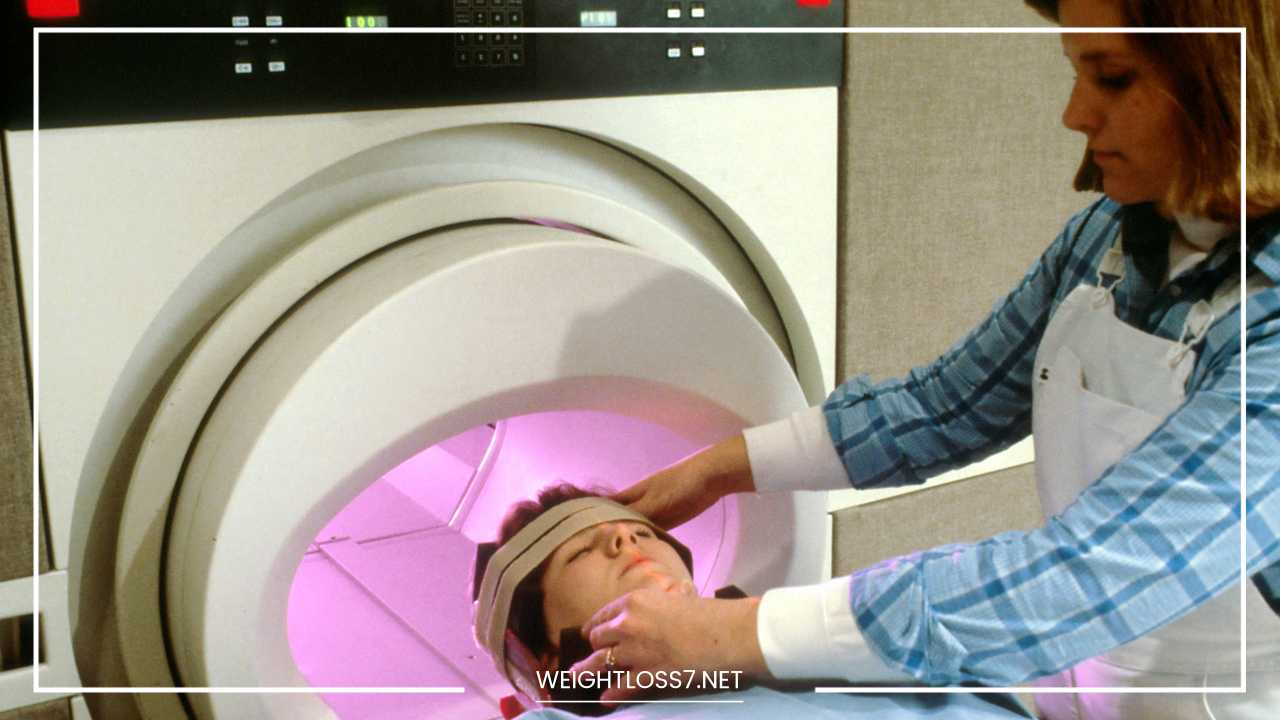
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRIs offer a different perspective on the internal landscape. They use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of organs, soft tissues, and bones. MRIs provide excellent contrast between different tissues, making them ideal for examining the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and joints. Unlike CT scans, MRIs don’t use radiation, but the enclosed machine can be uncomfortable for some patients, especially those with claustrophobia.
-
Nuclear Medicine Scans: These tests involve injecting a small amount of radioactive material into the body. This radioactive tracer accumulates in specific organs or tissues based on their function. By detecting the distribution of the tracer, doctors can identify abnormalities. Nuclear medicine scans are helpful for examining bone health, heart function, and certain cancers. It’s important to note that these tests involve low levels of radiation exposure.
Behind the Scenes: The Imaging Test Experience
If your doctor has recommended an imaging test, here’s a general breakdown of what to expect:
-
Consultation: The journey begins with a discussion with your doctor. They’ll review your medical history, symptoms, and the reason for the test. They’ll explain the specific imaging test chosen, its benefits, and any potential risks. This is an excellent time to ask any questions you might have.
-
Preparation: Depending on the type of test, there might be some preparation involved. For example, you might be asked to remove certain clothing or jewelry that could interfere with the images. You might also need to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before an ultrasound of your abdomen. The technologist performing the test will provide specific instructions based on the type of imaging you’re undergoing.
-
The Procedure: On the day of the test, a trained technologist will guide you through the process. They’ll explain what to expect and answer any questions you have. During the procedure itself, it’s crucial to follow the technologist’s instructions carefully. This might involve lying still on a table, holding your breath for a moment, or changing positions. Some tests, like MRIs, might require you to wear headphones to block out loud noises from the machine.
-
Results: After the test is complete, the images are sent to a radiologist, a doctor specializing in interpreting imaging studies. The radiologist will analyze the images, create a report with their findings, and send it to your doctor. Your doctor will then schedule an appointment to discuss the results with you and explain what they mean in the context of your overall health.
Beyond the Basics: Addressing Common Concerns
While imaging tests offer tremendous benefits, it’s natural to have some concerns. Here are some commonly raised questions addressed:
-
Radiation Exposure: Some imaging tests, like X-rays and CT scans, involve a small amount of radiation exposure. The amount of radiation varies depending on the specific test. It’s important to remember that the benefits of the test often outweigh the minimal risks associated with radiation exposure. However, if you’re pregnant or concerned about radiation, discuss this with your doctor. They might suggest alternative imaging options or take steps to minimize radiation exposure.
-
Claustrophobia: If you experience claustrophobia, an MRI scan’s enclosed environment might cause anxiety. Talk to your doctor beforehand. Some centers offer open MRI machines, which are less confining. Additionally, medication might be an option to help manage anxiety during the scan.
-
Cost: Imaging tests can be expensive. The cost can vary depending on the type of test, the facility where it’s performed, and your insurance coverage. Discuss the cost with your doctor and insurance provider beforehand to understand what your out-of-pocket expenses might be.
The Future of Imaging: A Glimpse Ahead
The field of medical imaging is constantly evolving. New technologies are emerging, offering even more accurate and detailed views of the human body. Here are some exciting advancements to keep an eye on:
- Advanced Image Analysis: Artificial intelligence is playing an increasingly prominent role in medical imaging. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of imaging data to identify subtle abnormalities that might be missed by the human eye. This can lead to earlier diagnoses and improved patient outcomes.
- Molecular Imaging: This emerging field focuses on visualizing biological processes at the molecular level. Molecular imaging techniques can help identify diseases in their earliest stages, allowing for more targeted treatment approaches.
- Personalized Medicine: Imaging is becoming a cornerstone of personalized medicine. By analyzing detailed images of a patient’s body, doctors can tailor treatment plans to their specific needs and genetic makeup.
Empowering Yourself: Additional Tips for Navigating Imaging Tests
Going through an imaging test can feel like venturing into unfamiliar territory. Here are some additional tips to empower yourself and ensure a smooth experience:
- Be Informed: Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor questions about the specific imaging test recommended for you. Understand why the test is necessary, what information it’s expected to provide, and the potential risks and benefits involved.
- Gather Information: Once you know the type of imaging test, do some research online (on reputable medical websites) to familiarize yourself with the procedure. This can help alleviate any anxiety you might have.
- Communicate Clearly: Inform your doctor about any allergies you have or medications you’re taking. Also, mention any claustrophobia concerns or physical limitations that might affect your ability to stay still during the test.
- Bring Comfort Items: For some tests, like MRIs, you might be in the machine for a while. If allowed, bring a blanket or wear comfortable clothing to help you relax. For claustrophobia concerns, discuss relaxation techniques or medication options with your doctor beforehand.
- Take Notes: After your consultation with the radiologist, take notes or record the discussion. This can be helpful when processing the information later and discussing it with your doctor.
- Advocate for Yourself: Don’t be afraid to ask questions and clarify any doubts you have throughout the process. It’s your health, and you deserve to be fully informed and involved in your care.
Remember: You are a partner in your healthcare journey. By understanding the role of imaging tests and asking thoughtful questions, you can ensure you receive the best possible care.
Beyond Diagnosis: Additional Applications of Imaging
While diagnosing medical conditions is a primary function of imaging tests, their applications extend beyond that:
- Image-Guided Procedures: Imaging plays a crucial role in guiding minimally invasive procedures. For example, during a biopsy, an ultrasound or CT scan can be used to precisely locate the area of concern and guide the needle for tissue sampling.
- Monitoring Treatment: Imaging tests can be used to track the effectiveness of ongoing treatment, such as monitoring tumor shrinkage after chemotherapy or assessing bone healing after a fracture.
- Surgical Planning: Detailed images from CT scans or MRIs help surgeons plan complex surgeries by providing a virtual map of the area to be operated on. This allows for more precise and efficient procedures.
Final Word
Medical imaging is a powerful and versatile tool that has revolutionized modern medicine. By offering a window into the human body, it empowers doctors to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions more effectively.
As you navigate your healthcare journey, understanding the different imaging tests available and their applications can equip you to make informed decisions and feel more confident about your care.
Remember, open communication with your doctor is key to a smooth and successful experience with any imaging test.