What Are Unsaturated Fats
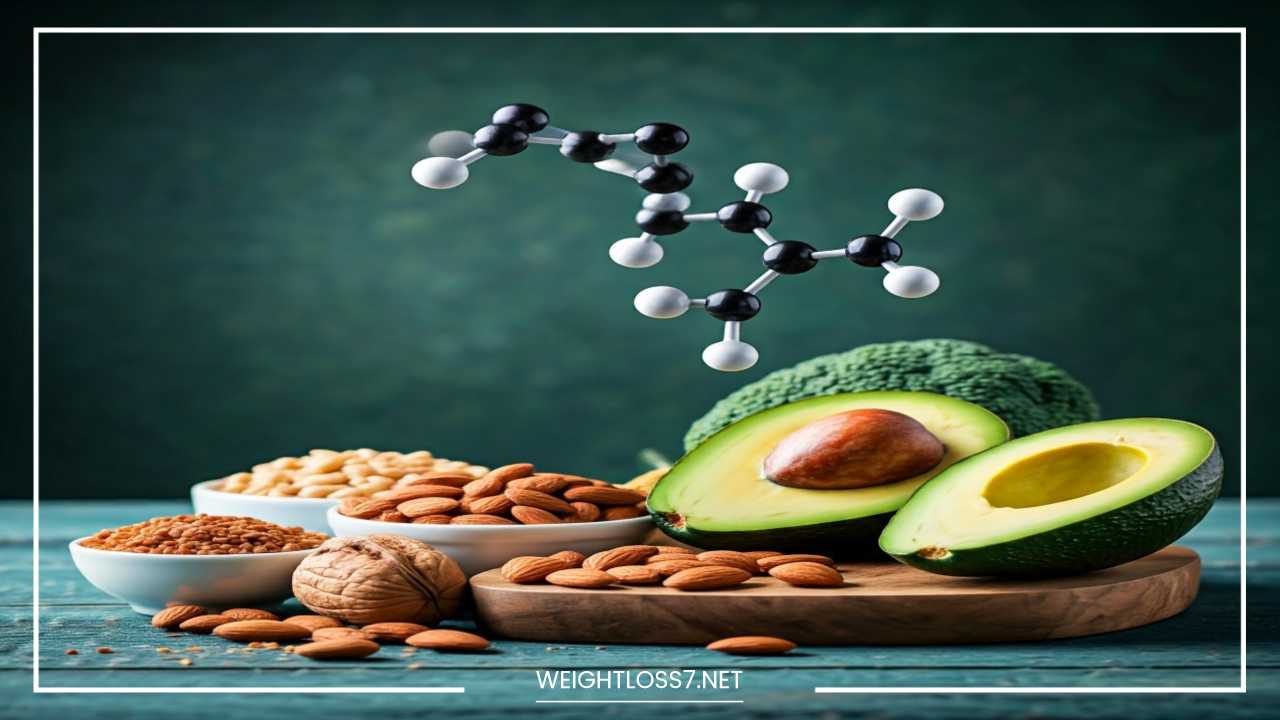

Unsaturated Fats
Understanding Unsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats are a category of dietary fat distinguished by their molecular structure, which includes one or more double bonds between carbon atoms.
This structural difference sets them apart from saturated fats, which consist solely of single bonds. The presence of double bonds in unsaturated fats not only influences their physical properties—making them typically liquid at room temperature—but also significantly impacts their health implications.
Chemical Structure and Types of Unsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats can be broadly categorized into two primary types: monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats. Each type offers unique benefits and sources, contributing to a balanced and healthful diet.
Monounsaturated Fats
Monounsaturated fats contain a single double bond in their fatty acid chain. Their chemical structure is associated with various health benefits, including improved heart health and weight management. Common dietary sources of monounsaturated fats include:
- Olive Oil: A staple in Mediterranean cuisine, olive oil is rich in antioxidants and has been extensively studied for its heart-healthy properties.
- Avocados: Packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, avocados are versatile and can be used in salads, smoothies, or as spreads.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and pecans are excellent sources of monounsaturated fats, providing a satisfying crunch and essential nutrients.
- Seeds: Pumpkin seeds and sunflower seeds are not only nutritious but also add texture to dishes.
Polyunsaturated Fats
Polyunsaturated fats have two or more double bonds in their structure and are further divided into two primary categories: omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These essential fats are crucial for various bodily functions and must be obtained from dietary sources. Key sources include:
- Fatty Fish: Varieties such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are exceptionally rich in omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
- Flaxseeds: These tiny seeds are a powerhouse of nutrients and are particularly high in ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), a type of omega-3.
- Chia Seeds: Similar to flaxseeds, chia seeds are an excellent source of ALA and are rich in fiber and protein.
- Walnuts: A convenient snack that is packed with omega-3s, walnuts can also enhance salads and baked goods.
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: While also essential, omega-6 fatty acids are often consumed in excess in the Western diet. Important sources include:
- Vegetable Oils: Oils such as corn, soybean, and sunflower are rich in omega-6 fatty acids and commonly used in cooking and processed foods.
- Nuts and Seeds: In addition to their omega-3 content, many nuts and seeds also provide omega-6 fatty acids, contributing to a balanced fat intake.
Health Benefits of Unsaturated Fats
The consumption of unsaturated fats has been linked to numerous health benefits. Here are some of the most notable:
Heart Health
Perhaps the most well-established benefit of unsaturated fats is their positive effect on heart health. Research consistently shows that both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can help improve cardiovascular health by:
- Lowering Bad Cholesterol (LDL): Unsaturated fats can reduce levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, the “bad” cholesterol that contributes to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Raising Good Cholesterol (HDL): High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol is considered “good” cholesterol, as it helps transport cholesterol away from the arteries and back to the liver for excretion. Higher HDL levels are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
- Reducing Triglycerides: Elevated triglyceride levels are another risk factor for heart disease. Unsaturated fats can help keep triglyceride levels in check.
- Decreasing Blood Pressure: Studies have shown that diets rich in unsaturated fats, particularly those high in omega-3s, can lead to reduced blood pressure levels, contributing to overall heart health.
Incorporating unsaturated fats into your diet can therefore be an effective strategy for reducing the risk of heart disease and related conditions.
Brain Health
Unsaturated fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, play a critical role in maintaining brain health. The brain is composed largely of fat, and the type of fat consumed can significantly impact cognitive function and overall mental well-being. Key benefits include:
- Supporting Cognitive Function: Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for the growth and maintenance of neuronal structures. Studies suggest that higher omega-3 intake is associated with better cognitive performance and a lower risk of cognitive decline.
- Improving Memory: Omega-3s may enhance memory and learning capabilities. Some research indicates that individuals with higher levels of omega-3s in their blood perform better on memory tests.
- Mood Regulation: There is evidence to suggest that omega-3 fatty acids can play a role in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. They may help stabilize mood by influencing neurotransmitter function.
Given the crucial role of fat in brain health, including sources of unsaturated fats in your diet can support cognitive function throughout life.
Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a common underlying factor in many health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Unsaturated fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties:
- Mitigating Inflammatory Responses: Omega-3s can compete with omega-6 fatty acids for metabolic enzymes, leading to a reduction in the production of pro-inflammatory compounds. This can help alleviate symptoms associated with inflammatory conditions.
- Supporting Joint Health: Omega-3s have been shown to reduce stiffness and joint pain in people with arthritis. Regular consumption may improve overall joint function and mobility.
Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet can help maintain a healthy inflammatory balance in the body.
Weight Management
While fats are calorie-dense, unsaturated fats can be beneficial for weight management when consumed in moderation. Here’s how they can assist:
- Promoting Satiety: Unsaturated fats can enhance feelings of fullness and satisfaction after meals, which may reduce overall calorie intake and help prevent overeating. Foods rich in healthy fats often take longer to digest, contributing to prolonged feelings of fullness.
- Encouraging Healthier Food Choices: By adding flavor and texture to meals, unsaturated fats can make healthy foods more enjoyable, increasing the likelihood of making better dietary choices overall.
In the context of a balanced diet, incorporating unsaturated fats can support weight management efforts.
Sources of Unsaturated Fats
There are numerous delicious and nutritious sources of unsaturated fats that can be easily integrated into daily meals. Below are detailed lists of foods rich in both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats:
Foods High in Monounsaturated Fats
- Olive Oil: Ideal for salad dressings, sautéing, or drizzling over dishes.
- Avocados: Use in salads, smoothies, or as a spread on toast.
- Nuts: Almonds, hazelnuts, and pecans can be enjoyed as snacks, in granola, or as toppings for yogurt and salads.
- Seeds: Pumpkin seeds and sesame seeds can add crunch and nutrition to various dishes.
Foods High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Fatty Fish: Aim for varieties such as salmon, sardines, mackerel, and trout for a rich source of omega-3s.
- Flaxseeds: Ground flaxseeds can be added to smoothies, oatmeal, or baked goods.
- Chia Seeds: These tiny seeds can be soaked in water or milk to create a nutritious pudding or added to smoothies and cereals.
- Walnuts: Enjoy as a snack, sprinkle on salads, or incorporate into baked goods.
Foods High in Omega-6 Fatty Acids
- Vegetable Oils: Common cooking oils like corn, sunflower, and soybean oil are rich in omega-6 fatty acids.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and pine nuts contribute omega-6s to your diet.
Incorporating Unsaturated Fats into Your Diet
To maximize the health benefits of unsaturated fats, consider the following practical tips for incorporating them into your daily meals:
- Cook with Healthy Oils: Substitute butter and margarine with olive oil, avocado oil, or flaxseed oil. These oils are excellent for cooking, salad dressings, and drizzling over finished dishes.
- Eat Fatty Fish Regularly: Incorporate at least two servings of fatty fish into your weekly meal plan. Try grilling, baking, or steaming for a flavorful and nutritious option.
- Snack on Nuts and Seeds: Keep a variety of nuts and seeds on hand for quick snacks. They are nutrient-dense and can help satisfy cravings between meals.
- Include Avocados in Your Meals: Avocados can be added to smoothies for creaminess, spread on toast, or used in salads for a nutritional boost.
- Read Food Labels: When shopping, pay attention to food labels. Choose products low in saturated and trans fats while high in unsaturated fats.
- Experiment with Recipes: Incorporate unsaturated fats into your favorite recipes. For instance, use olive oil in dressings or marinades, or add nuts and seeds to baked goods and salads.
Balancing Unsaturated Fats
While unsaturated fats are generally healthier than saturated fats, moderation is key. Here are some tips to ensure a balanced intake:
- Mind Portion Sizes: Even healthy fats can contribute to excess calorie intake if consumed in large quantities. Pay attention to serving sizes, especially when snacking on nuts and seeds.
- Diverse Fat Sources: Aim for a variety of unsaturated fats in your diet to ensure a broad spectrum of nutrients. This can also help prevent boredom with meals.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how different foods affect your energy levels and overall well-being. Adjust your intake based on your personal needs and preferences.
Common Misconceptions About Fats
Despite the numerous health benefits of unsaturated fats, several misconceptions persist regarding dietary fats in general. Let’s address some common myths:
- All Fats Are Bad: This is one of the most widespread misconceptions. While trans fats and excessive saturated fats can harm health, unsaturated fats are beneficial and essential for bodily functions.
- Eating Fat Makes You Fat: While fat is calorie-dense, consuming healthy fats in moderation can actually support weight management by promoting satiety and enhancing the flavor of nutritious foods.
- You Should Avoid All Oils: Many people believe that oils should be completely avoided for weight loss. However, incorporating healthy oils, such as olive oil, can actually enhance your diet and provide essential nutrients.
Final Thoughts
Unsaturated fats are vital components of a healthy diet, offering numerous benefits for heart health, brain function, inflammation reduction, and weight management.
By consciously incorporating more unsaturated fats into your meals—through healthy oils, fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and avocados—you can significantly improve your overall well-being.
Remember that balance and moderation are essential; aim for a varied intake of these healthy fats to reap their full benefits.
Embracing unsaturated fats not only enhances the flavor and enjoyment of your meals but also represents a positive investment in your long-term health.
Always consider consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice tailored to your individual health needs and goals.
Please note: This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.